Today, i had problem wtih my trunking cisco catalyst c2950. one of my access port to fibre optic interconnection was problem. after one hour i try to find solution for this matter.
this is log problem show:
%SPANTREE-7-RECV_1Q_NON_TRUNK: Received 802.1Q BPDU on non trunk FastEthernet0/1 VLAN2.
004964: May 4 00:01:17.302: %SPANTREE-7-BLOCK_PORT_TYPE: Blocking FastEthernet0/1 on VLAN0002. Inconsistent port type.
status of the port show that operational mode change into trunk (before access).
#sh int fa0/1 switchport
Name: Fa0/1
Switchport: Enabled
Administrative Mode: dynamic desirable
Operational Mode: trunk
Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q
Operational Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q
Negotiation of Trunking: On
Access Mode VLAN: 2 (VLAN0002)
Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default)
Administrative private-vlan host-association: none
Administrative private-vlan mapping: none
Operational private-vlan: none
Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL
Pruning VLANs Enabled: 2-1001
After i change to static access it’s running again
#sh int fa0/1 switchport
Name: Fa0/1
Switchport: Enabled
Administrative Mode: static access
Operational Mode: static access
Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q
Operational Trunking Encapsulation: native
Negotiation of Trunking: Off
Access Mode VLAN: 2 (VLAN0002)
Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default)
Administrative private-vlan host-association: none
Administrative private-vlan mapping: none
Operational private-vlan: none
Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL
Pruning VLANs Enabled: 2-1001
In the majority of cases, the reason for detection of STP inconsistency on the port is apparent:
Access port receives an IEEE 802.1Q-tagged SSTP BPDU.
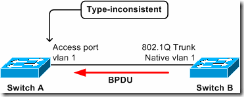
In this scenario, access port on bridge A receives, from bridge B, a tagged PVST+ BPDU from STP of a VLAN other than 1. The port on A will be put into type-inconsistent state.
Note: The switches need not be connected directly; if they are connected through one or more IEEE 802.1D or IEEE 802.1Q switches—or even hubs—then the effect is the same.
IEEE 802.1Q trunking port receives an untagged SSTP BPDU with a VLAN type, length, value (TLV) that does not match the VLAN where the BPDU was received.

-
In this scenario, the trunk port on A receives a PVST+ BPDU from STP of VLAN 2 with a tag of VLAN 2. This triggers the port on A to be blocked in both VLAN 1 and VLAN 2.
If devices on both ends of a point-to-point link are Cisco Catalyst switches, an examination of the local and remote port configuration typically reveals the configuration mismatch:
-
The port is configured for IEEE 802.1Q trunking on one side but the other side is access port.
-
IEEE 802.1Q trunks are on both sides, but the Native VLANs are different.
In these cases, fix the configuration mismatch to resolve the STP inconsistency.